Get a monitor and contributor to air quality data in your city.
93.6K people follow this city





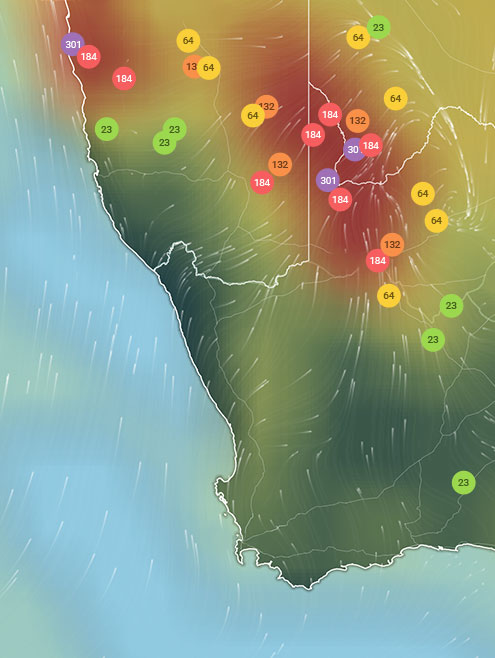
AIR QUALITY DATA CONTRIBUTORS
Find out more about contributors and data sources| Weather | Broken clouds |
| Temperature | 53.6°F |
| Humidity | 80% |
| Wind | 4.6 mp/h |
| Pressure | 30 Hg |
| # | city | US AQI |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Coyhaique, Aisen | 159 |
| 2 | Coronel, Biobio | 155 |
| 3 | Temuco, Araucania | 134 |
| 4 | Talcahuano, Biobio | 96 |
| 5 | Coquimbo, Coquimbo | 60 |
| 6 | Santiago, Santiago Metropolitan | 60 |
| 7 | Quintero, Valparaiso | 59 |
| 8 | Puchuncavi, Valparaiso | 55 |
| 9 | Quillota, Valparaiso | 47 |
| 10 | Concepcion, Biobio | 41 |
(local time)
SEE WORLD AQI RANKING
| # | station | US AQI |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Martin de Zamora | 116 |
| 2 | Parque O'Higgins | 72 |
| 3 | Lo B El Tranque | 69 |
| 4 | Lo B Los Manzanos | 69 |
| 5 | Penalolen Ichuac | 69 |
| 6 | Red_Universidades_MP_01 | 68 |
| 7 | Villa Las Margaritas | 64 |
| 8 | El Bosque | 63 |
| 9 | Jardin Jaraquemada El Bosque | 61 |
| 10 | Penalolen Cristo | 59 |
(local time)
SEE WORLD AQI RANKINGUS AQI
60
live AQI index
Moderate
| Air pollution level | Air quality index | Main pollutant |
|---|---|---|
| Moderate | 60 US AQI | PM2.5 |
| Pollutants | Concentration | |
|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | 16.3µg/m³ | |
| O3 | 14µg/m³ | |
| NO2 | 26.9µg/m³ | |
| SO2 | 5.2µg/m³ | |
| CO | 618.3µg/m³ | |
PM2.5
x3.3
PM2.5 concentration in Santiago is currently 3.3 times the WHO annual air quality guideline value
| Sensitive groups should reduce outdoor exercise | |
| Close your windows to avoid dirty outdoor air GET A MONITOR | |
| Sensitive groups should wear a mask outdoors GET A MASK | |
| Sensitive groups should run an air purifier GET AN AIR PURIFIER |
| Day | Pollution level | Weather | Temperature | Wind |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sunday, Apr 28 | Moderate 64 AQI US | 62.6° 50° | ||
| Monday, Apr 29 | Good 26 AQI US | 62.6° 51.8° | ||
| Tuesday, Apr 30 | Moderate 52 AQI US | 57.2° 50° | ||
| Today | Moderate 60 AQI US | 57.2° 50° | ||
| Thursday, May 2 | Good 36 AQI US | 59° 46.4° | ||
| Friday, May 3 | Good 45 AQI US | 62.6° 46.4° | ||
| Saturday, May 4 | Good 37 AQI US | 62.6° 50° | ||
| Sunday, May 5 | Good 41 AQI US | 62.6° 50° | ||
| Monday, May 6 | Good 50 AQI US | 59° 46.4° | ||
| Tuesday, May 7 | Good 50 AQI US | 50° 39.2° |
Interested in hourly forecast? Get the app
Santiago is also known as Santiago de Chile and is the capital and largest city of Chile as well as one of the largest cities in the Americas. It was named after the biblical figure of St. James who is the patron saint of Spain. It is located entirely in the central valley and is home to an estimated population of 7 million. The majority of which live in the densely-populated urban area. The fast-flowing Mapocho River flows through the valley and Santiago stands on both sides of it.
The mighty Andes mountain range can be seen from nearly all parts of the city, but the close proximity to this creates the problem of lingering smog, especially during the winter months when there is less rainfall.
In the second quarter of 2021, Santiago was experiencing a period of “Moderate” air quality with a US AQI reading of 87. This classification is in line with recommendations by the World Health Organisation (WHO). The concentration of PM2.5 was 29.3 µg/m³. With a level such as this, it is advisable to close doors and windows to prevent the ingress of dirty air into the rooms and those of a sensitive disposition are advised against outdoor activity until the air quality shows signs of improvement.
For 8 months of the year in 2020, Santiago reported “Moderate” levels of air quality with figures between 12.1 and 35.4 µg/m³. For the summer months of May, June and July, the quality was slightly worse when the category entered the “Unhealthy for sensitive groups” with figures between 35.5 and 55.4 µg/m³. For the remaining month of December, Santiago saw an improvement with readings between 10 and 12 µg/m³.
Looking back at records from previous years it can be seen that the air quality remains about the same. In 2017 the annual average figure was 23.1 µg/m³, followed by 29.4 µg/m³ the following year. 2019 saw a slight improvement with a mean reading of 27.7 µg/m³, before showing a marked improvement of 23.6 µg/m³ in 2020.
The growth of air pollution stems from both increased industrialisation and environmental factors that continue to affect the region’s climate and are critical to the country’s health. As is common with many other cities throughout the world, the two main causes of polluted air are ozone (O3) and PM2.5.
The main contributors to the accumulation of PM2.5 are vehicle exhaust fumes, fossil-fuel-powered power stations and various industrial processes. Agricultural burning and ammonium emissions from agricultural processes are all a result of increased industrialisation in Chile’s main cities, especially Santiago.
The situation often deteriorates during the winter months due to the prevalence of firewood used to heat homes and business premises. Additionally, constructions zones, agricultural fields, and dirt roads produce detached sediment particles that are transported by the wind to the streets in the cities.
Because of Santiago’s position between two mountain ranges, the Andes and the Cordillera de la Costa, a pocket is created where stale air accumulates and takes longer to disperse.
Although carbon dioxide (CO2) is the main greenhouse gas (GHG) that contributes to global warming, there are other pollutants that also compound the problem. Due to their different characteristics to CO2, can also be an important part of the problem. One of them is the short-lived climate pollutant black carbon (BC) or soot. Black carbon contributes to global warming with a potential up to 1,500 times greater than carbon dioxide.
This pollutant is a major component of fine particulate matter, and in Chile, it comes mainly from the burning of firewood and from means of transportation.
There are many ways in which an individual can help to reduce air pollution.
The local government needs to encourage the purchase of electric vehicles, possibly by offering subsidies and ensuring there are suitable charging stations throughout the city. Above all, drivers need to have confidence in their new purchase.
Air pollutants contribute to a decrease in lung function and an increase in bronchial reactivity, decrease exercise tolerance and increase the risk of chronic obstructive bronchitis, pulmonary emphysema, exacerbation of bronchial asthma and lung cancer, amongst other effects. . In Chile, since 1980, studies have multiplied that demonstrate the effects of air pollution, especially particles, on daily mortality, respiratory symptoms and consultations. These studies, carried out first in Santiago and later in Temuco have confirmed the results reported in international publications that have established that for every 50 µg/m³ increase in PM10 levels in 24 hours, there is an average increase of about 3 per cent in general mortality. These studies have also detected that an increase in PM10 is associated with an increase in respiratory and cardiovascular mortality.
Another relevant fact is the presence of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), as components of the particulate material. These compounds are produced by the incomplete combustion of organic material (oil, gasoline, wood, coal and biomass in general). Numerous types of PAHs have been identified in the organic fraction of particulate matter in cities with high levels of atmospheric pollution; six of them have been classified as carcinogenic by the International Agency of Research on Cancer with benzo α-pyrene being the PAH most carcinogenic in cigarette smoke and in smog in highly polluted cities, such as Santiago.
7Contributors
Government Contributor

4 stations
Non-profit organization Contributor

10 stations
Educational Contributor

1 station
Individual Contributor

1 station
3 Anonymous Contributors

3 stations
3 Data sources